| CPC G05F 3/262 (2013.01) [H02M 1/08 (2013.01); H02M 1/32 (2013.01); H02M 3/158 (2013.01); H02M 1/0019 (2021.05); H02M 1/0022 (2021.05); H02M 3/1566 (2021.05)] | 20 Claims |
|
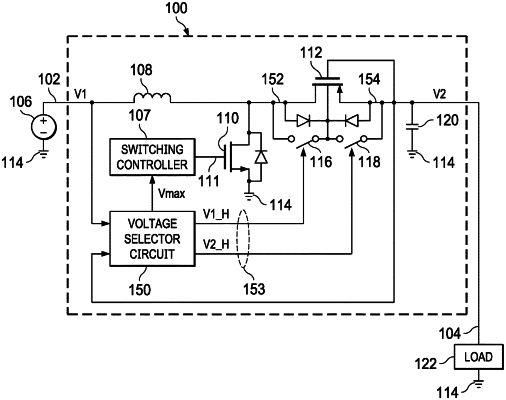
1. A voltage selector circuit, comprising:
a voltage comparator having first and second comparator inputs and a comparator output, wherein the first comparator input is coupled to a first input voltage terminal, the second comparator input is coupled to a second input voltage terminal, the first input voltage terminal is configured to provide a first input voltage signal, and the second input voltage terminal is configured to provide a second input voltage signal;
a multiplexer having a multiplexer input and a multiplexer output, wherein the multiplexer input is coupled to the comparator output, and the multiplexer is configured to select a larger signal of the first input voltage signal and the second input voltage signal, and provide the larger signal at the multiplexer output; and
an adaptive current bias generator configured to generate a bias current for the voltage comparator during a transition from a first state to a second state, wherein the first input voltage signal is continuously larger than the second input voltage signal during the first state, and the second input voltage signal is continuously larger than the first input voltage signal in the second state, the bias current during the transition having a time-varying current level that is proportional to a time-varying difference between the first input voltage signal and the second input voltage signal during the transition.
|