| CPC B01L 3/502792 (2013.01) [B01L 2300/0645 (2013.01); B01L 2300/0654 (2013.01); B01L 2300/0887 (2013.01); B01L 2300/161 (2013.01); B01L 2400/0424 (2013.01); B01L 2400/0427 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
1. An electrokinetic device for moving an aqueous droplet, comprising:
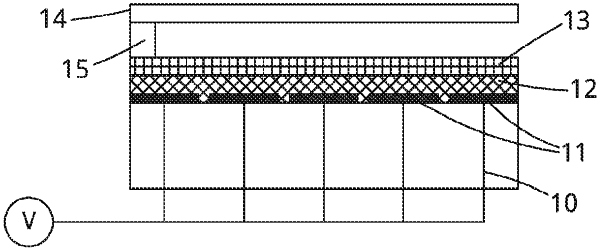
a first substrate having a matrix of electrodes, wherein each of the matrix of electrodes is coupled to a thin film transistor, and wherein the matrix of electrodes are overcoated with a functional coating comprising:
a dielectric in contact with the matrix of electrodes, the dielectric comprising a layer of aluminium oxide and a layer of hafnium oxide;
a conformal layer comprising parylene in contact with the dielectric, wherein the parylene is circa 100 nm in thickness;
a hydrophobic layer in contact with the conformal layer;
a second substrate comprising a top electrode and a second hydrophobic layer;
a spacer disposed between the first substrate and the second substrate and defining an electrokinetic workspace; and
a voltage source operatively coupled to the matrix of electrodes, the voltage source controllable to provide a differential electrical potential between a first matrix electrode and a second matrix electrode in order to move the aqueous droplet between the first matrix electrode and the second matrix electrode.
|