| CPC B01D 53/228 (2013.01) [B01D 71/028 (2013.01); C10L 3/104 (2013.01); C10L 2290/548 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
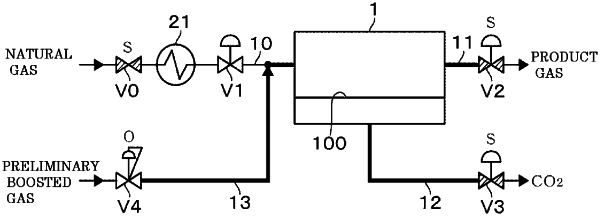
1. A carbon dioxide gas separation method of permeating carbon dioxide gas in a gas to be treated from a primary side to a secondary side of a separation membrane provided in a separation membrane module to reduce the carbon dioxide gas in the gas to be treated, the method characterized by comprising:
a step of supplying a preliminary boosted gas to the primary side of the separation membrane to boost the pressure to a preliminary pressure between a stand-by pressure and an operating pressure, before the gas to be treated is supplied at a supply pressure higher than the stand-by pressure to the separation membrane module in a state of the stand-by pressure lower than the operating pressure when the carbon dioxide gas is permeated through the separation membrane, in order to maintain a temperature of the gas to be treated in which a decrease in pressure occurs to a temperature higher than a condensation temperature of the carbon dioxide gas or a solidification temperature of the carbon dioxide gas;
a subsequent step of supplying the gas to be treated to the separation membrane module to increase the pressure of the separation membrane module to the operating pressure and to reduce the carbon dioxide gas in the gas to be treated; and
wherein the preliminary pressure is a pressure of Ppre or higher defined by the following Formula (1) to Formula (3) when the operating pressure is designated as POpe, a vapor pressure of the carbon dioxide gas at 20° C. is designated as PVap, and a concentration (molar ratio) of the carbon dioxide gas in the gas to be treated is designated as CCO2, in which unit of measurement of pressure for each of said pressures is MPaG:
ln(PPre)=a×[1/[(POpe/PVap)2+(POpe/PVap)3]]+b Formula (1)
a=0.1318×(CCO2)−13.63 Formula (2)
b=0.8886×ln(CCO2)−2.372 Formula (3).
|