| CPC H04L 63/1416 (2013.01) [H04L 63/1425 (2013.01); H04L 63/1441 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method, comprising:
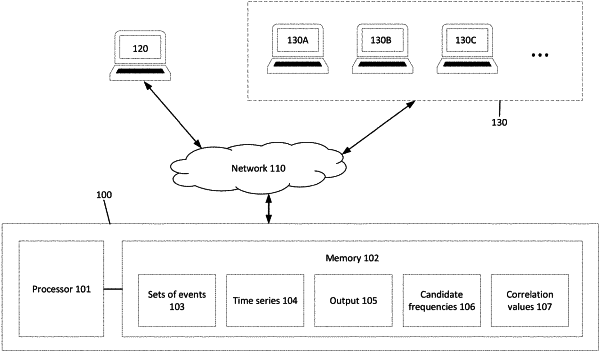
receiving, via a processor, an indication of a plurality of sets of events from a time period, the plurality of sets of events associated with a first device, each set of events from the plurality of sets of events associated with the first device and a second device from a plurality of second devices that is different for remaining sets of events from the plurality of sets of events and does not include the first device, each event for each set of events from the plurality of sets of events associated with a start time, an end time, a value indicating significance of that event, and a plurality of attributes;
converting, via the processor, the plurality of sets of events into a time series based on the value for each event from each set of events from the plurality of sets of events, the start time for each event from each set of events from the plurality of sets of events, and the end time for each event from each set of events from the plurality of sets of events;
normalizing, via the processor, the time series to generate a normalized time series;
performing, via the processor, a discrete Fourier transform using the normalized time series to generate an output that is associated with a plurality of frequencies and a plurality of magnitude values, each frequency from the plurality of frequencies associated with a magnitude value from the plurality of magnitude values;
selecting, via the processor, a set of candidate frequencies from the plurality of frequencies potentially exhibiting periodic behavior;
generating, via the processor, a set of correlation values based on a comparison between each set of events from the plurality of sets of events and each candidate frequency from the set of candidate frequencies for correlation;
identifying, via the processor and based on the set of correlation values, an attribute that is from the plurality of attributes associated with an event from a set of events from the plurality of sets of events and that is predicted to cause the periodic behavior; and
sending, via the processor, a signal to cause an output including representation of the attribute.
|