| CPC H02P 27/085 (2013.01) [H02M 7/5395 (2013.01); H02P 21/22 (2016.02)] | 14 Claims |
|
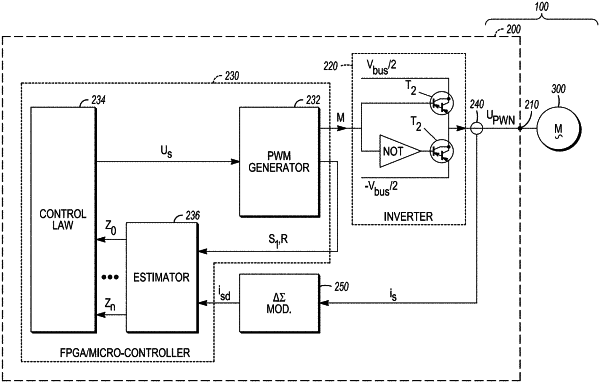
1. A variable speed drive for the closed loop control of the operation of an AC electric motor based on a given control law, the variable speed drive comprising:
an output terminal for delivering a controlled alternating drive voltage to the controlled AC electric motor;
a solid-state power inverter including solid-state switches for generating the drive voltage by commutating the solid-state switches to invert a provided DC voltage;
a drive controller for controlling the generation of the drive voltage by the power inverter; and
a drive current sensing device for measuring the instantaneous intensity of the drive current taken up by the controlled AC electric motor, and for providing the resulting measurements as a drive current intensity signal to the drive controller, wherein the drive controller includes:
a pulse-width modulation generator;
a control law module storing the given control law; and
a state variable estimation module for estimating the instantaneous value of at least one state variable of the controlled AC electric motor,
wherein the control law module is adapted to, based on the stored control law and state variable estimates provided by the estimation module, compute a target voltage signal and output the computed target voltage signal to the pulse-width modulation generator,
wherein the pulse-width modulation generator is adapted to:
approximate the received target voltage signal with a pulse-width modulated inverter control signal;
control the operation of the power inverter using the inverter control signal, thereby obtaining the drive voltage;
compute, based on the deviation between the inverter control signal and the target voltage signal, a state variable estimation support signal;
extract, from the inverter control signal, a time sequence of the next commutations of the power inverter's solid-state switches; and
output the computed state variable estimation support signal and the extracted commutation time sequence to the state variable estimation module, and wherein the state variable estimation module is adapted to:
estimate the instantaneous value of a state variable of the AC electric motor based on the received state variable estimation support signal and the drive current intensity signal provided by the drive current sensing device wherein those time segments of the drive current intensity signal, which, according to the received commutation time sequence, correspond to the commutation of one of the power inverter's solid-state switches, are discarded in the state variable estimation as corrupted time segments; and
output the resulting state variable estimate to the control law module.
|