| CPC G10L 19/038 (2013.01) [G10L 19/028 (2013.01); G10L 25/18 (2013.01); G10L 25/21 (2013.01); G10L 25/30 (2013.01)] | 3 Claims |
|
1. A processing method comprising:
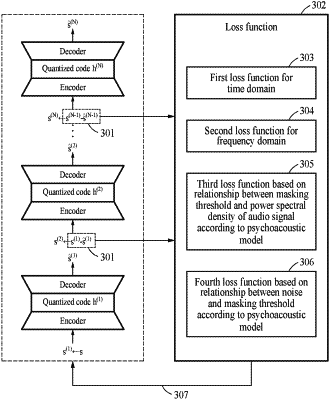
acquiring a final audio signal for an initial audio signal using a plurality of neural network models generating output audio signals by encoding and decoding input audio signals;
acquiring a masking threshold and a power spectral density for the initial audio signal through a psychoacoustic model;
determining a weight based on a relationship between the masking threshold and the power spectral density for each frequency;
calculating a difference between a power spectral density of the initial audio signal and a power spectral density of the final audio signal for each frequency based on the determined weight;
training the neural network models based on a result of the calculating; and
generating a new final audio signal distinguished from the final audio signal from the initial audio signal using the trained neural network models,
wherein the plurality of neural networks is in a consecutive relationship, where an i-th neural network model generates an output audio signal using, as an input audio signal, a difference between an output audio signal of an (i−1)-th neural network model and an input audio signal of the (i−1)-th neural network model
wherein the masking threshold is a criterion for masking noise generated in an encoding and decoding process of the plurality of neural network models, respectively.
|