| CPC G10K 11/17854 (2018.01) [G10K 11/17823 (2018.01); G10K 11/17825 (2018.01); G10K 11/17881 (2018.01); H04R 1/1083 (2013.01); G10K 2210/1081 (2013.01); G10K 2210/3026 (2013.01); G10K 2210/3027 (2013.01); G10K 2210/3044 (2013.01); G10K 2210/3048 (2013.01); H04R 2460/01 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
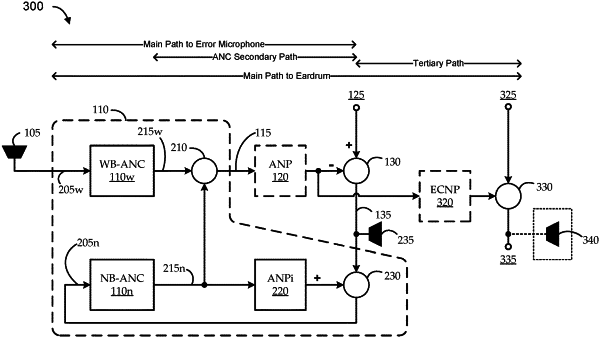
1. A method for ear cavity frequency response (EFCR) adaptive noise cancelation (ANC) with path-compensation over an entire main path to the eardrum (MPED), the method comprising:
receiving, while a user is wearing a headphone earpiece to manifest a present wearer/wearing condition relative to an outer ear of the user, a reference noise signal representing ambient noise at an out-facing side of the headphone earpiece, an anti-noise signal generated by an ANC system of the headphone earpiece using a present ANC filter configuration to cancel an in-ear noise signal corresponding to the ambient noise as manifest at a target location at an in-facing side of the headphone earpiece due to acoustical path effects of the MPED, and a residual noise signal representing a combination of the anti-noise signal and the in-ear noise signal;
for each kth pre-trained ANC model of K pre-trained ANC models, each having a kth anti-noise path (ANP) filter model and a kth MPED filter model previously trained on a kth trained wearer/wearing condition, K being a positive integer greater than one:
computing a kth estimated actual noise signal by using the kth ANP filter model to transform the anti-noise signal into a path-compensated anti-noise signal, and removing the path-compensated anti-noise signal from the residual noise signal;
computing a kth estimated eardrum noise signal by using the kth MPED filter model to transform the reference noise signal; and
computing a kth candidate residual noise between the kth estimated actual noise signal and the kth estimated eardrum noise signal;
selecting one of the pre-trained ANC models as yielding the lowest kth candidate residual noise; and
directing the ANC system of the headphone earpiece to replace the present ANC filter configuration with a new ANC filter configuration based on the selected one of the pre-trained ANC models.
|