| CPC E21B 34/066 (2013.01) [E21B 2200/04 (2020.05)] | 20 Claims |
|
14. A method comprising:
receiving a valve control signal from a wireless telemetry system;
receiving electric power from a primary cell or a rechargeable battery pack;
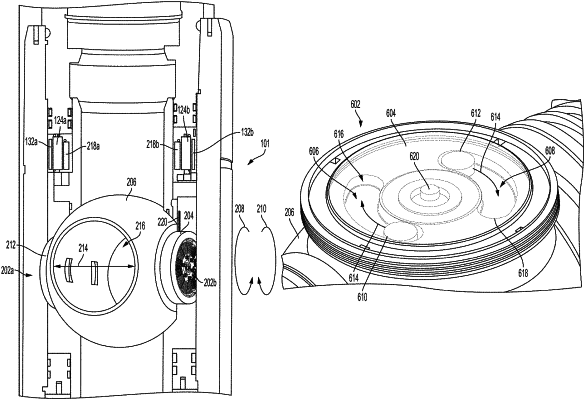
providing an actuation force to a ball valve positionable downhole within a fluid flow path of a wellbore using an electric motor, wherein the electric motor is coupleable to a drive system of the ball valve within a trunnion of the ball valve with a pin that is rotatable by the electric motor within a slot, the electric motor being powered by the electric power, wherein the electric motor is operable to rotate the pin within the slot prior to the pin engaging the drive system; and
moving the ball valve between an open position and a closed position using the actuation force, wherein in the open position, a fluid is able to flow through a through-bore of the ball valve, and in the closed position, the fluid is prevented from flowing through the through-bore.
|