| CPC C02F 9/00 (2013.01) [C02F 1/66 (2013.01); C02F 3/286 (2013.01); C02F 11/04 (2013.01); C02F 11/12 (2013.01); C02F 2101/105 (2013.01); C02F 2301/106 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
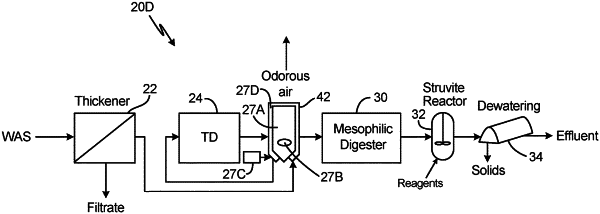
1. A waste treatment process comprising:
supplying waste activated sludge to a thermophilic digester;
processing the waste activated sludge in a thermophilic digester to produce a thermophilic digestate;
increasing pH of the thermophilic digestate downstream of the thermophilic digester;
concurrently with increasing pH of the thermophilic digestate and prior to any other processing, cooling the thermophilic digestate in a heat exchanger/air stripper;
wherein increasing pH of the thermophilic digestate downstream of the thermophilic digester inhibits struvite scaling during cooling the thermophilic digestate in the heat exchanger; and
separating struvite from the treated digestate.
|