| CPC B29C 64/165 (2017.08) [B29C 64/209 (2017.08); B29C 64/273 (2017.08); B29C 64/282 (2017.08); B33Y 10/00 (2014.12); B33Y 70/10 (2020.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
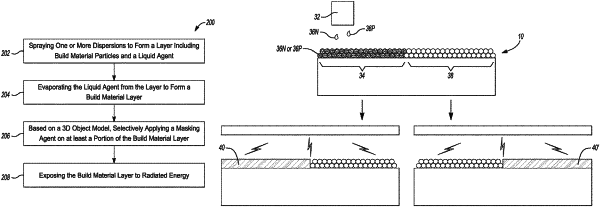
1. A method for three-dimensional (3D) printing, comprising:
spraying one or more dispersions to form a layer including build material particles and a liquid agent;
evaporating the liquid agent from the layer to form a build material layer;
based on a 3D object model, selectively applying a masking agent on at least a portion of the build material layer; and
exposing the build material layer to radiated energy;
wherein the build material particles are selected from the group consisting of metal, ceramic, a mixture of two or more metals, a mixture of a metal and a ceramic, and combinations thereof;
and wherein the build material particles have a D50 particle size distribution value ranging from about 15 μm to about 100 μm.
|