| CPC A61B 8/5207 (2013.01) [A61B 8/0841 (2013.01); A61B 8/4483 (2013.01); A61B 8/461 (2013.01); A61B 8/54 (2013.01); A61B 17/3403 (2013.01); G06T 7/0012 (2013.01); A61B 2017/3413 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10132 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30061 (2013.01)] | 2 Claims |
|
1. A combined method for analyzing, identifying, tracking, ranging and displaying pleura breath signal in sub-millimeter-scale resolution, with its steps including:
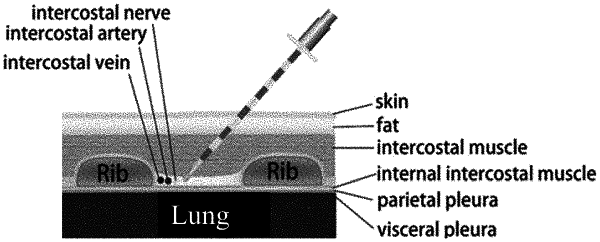
(a) obtaining a plurality of echo ultrasonic signals from the axial depth direction of tissue puncture at least 20 times per second by an ultrasound probe, placed in the inner side of a puncture needle and coaxial with the puncture needle, wherein, each echo ultrasonic signal includes an ultrasonic amplitude and a time difference between emission and reception of ultrasonic wave, wherein the ultrasound probe transmits and receives signals coaxially, wherein the tissue puncture refers to a region from an intercostal space to the pleura; the ultrasound probe measures the distance between the tip of the puncture needle and the innermost intercostal muscle (IiM) and between the tip of the puncture needle and the pleura in real time during the breathing;
(b) transforming the time differences between emission and reception of ultrasonic wave into a plurality of axial distances, the axial distances are a plurality of echo distances between various tissue interface and the ultrasound probe;
(c) using the axial distances and the ultrasonic amplitudes extracted from radio frequency signals to produce a distance and signal amplitude figure according to a length unit and an amplitude unit;
(d) based on the distance and signal amplitude figure, setting a region of interest according to a specific amplitude variation feature and a specific depth variation feature, identifying a flickering pleura signal, then instantly displaying and tracking the dynamic distances between a tip of the puncture needle and the pleura;
(e) within an operation period, repeating the operational steps (a) to (c), using different axial depths to obtain a plurality of distance and signal amplitude figures;
(f) based on the distance and signal amplitude figures, obtaining a distance and signal time-varying figure according to the operation period; and
(g) based on the distance and signal time-varying figure, setting a region of interest according to the specific amplitude variation feature, the specific depth variation feature and a cyclic variation feature, then identifying the flickering pleura signal and displaying the dynamic distances between the pleura and the tip of the puncture needle.
|