| CPC H04W 4/029 (2018.02) [H04W 4/026 (2013.01); H04W 4/027 (2013.01); H04W 4/33 (2018.02)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. One or more non-transitory computer-readable media storing computer-executable instructions that upon execution cause one or more processors to perform acts comprising:
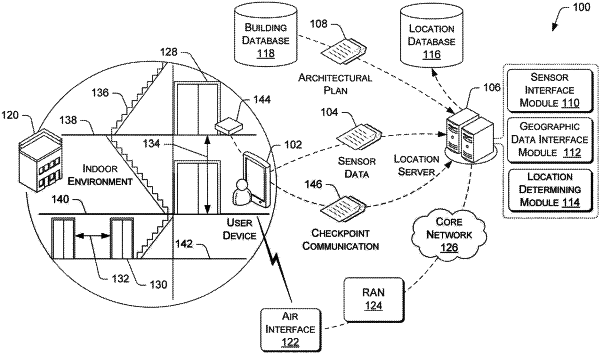
using a combination of an image sensor, light intensity, Wi-Fi radio, and a proximity sensor to determine that a user device is within an indoor environment;
determining a start position of the user device based at least on the user device's proximity to known locations of one or more checkpoint devices in the indoor environment;
receiving an indication of an acceleration event at the start position and a deceleration event at a finish position associated with the user device that is located in the indoor environment;
determining a traveled distance of the user device based at least on an amount of time elapsed between the acceleration event and the deceleration event;
obtaining sensor data collected during the time elapsed and associated with the user device;
determining a direction of travel of the user device based at least on the sensor data;
mapping, using an architectural plan associated with the indoor environment, the finish position relative to the start position of the user device in the indoor environment based at least on the traveled distance and the direction of travel;
predicting, using crowdsourced data aggregated from multiple user devices in the indoor environment, distances between floors in the indoor environment;
appending the predicted distances between floors to the architectural plan associated with the indoor environment; and
identifying a floor level corresponding to the finish position of the user device based at least on:
the start position,
the predicted distances between the floor levels or the terminals,
the traveled distance of the user device, and
the direction of travel of the user device.
|