| CPC H04L 9/3265 (2013.01) [H04L 9/0825 (2013.01); H04L 9/0852 (2013.01); H04L 9/3247 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
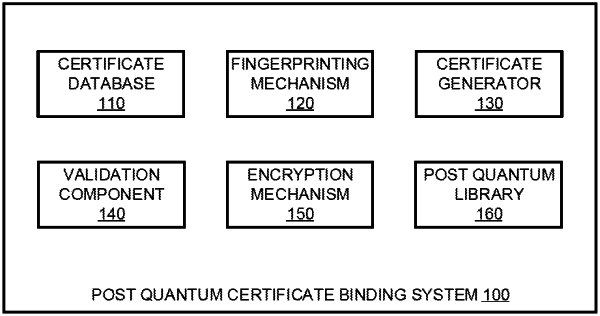
1. A computer-implemented method of binding post-quantum certificates to traditional certificates, the computer-implemented method comprising:
selecting a first traditional certificate in a certificate chain owned by an owner;
calculating a first digital fingerprint of the first traditional certificate using a cryptographic hash function on characteristics found within the first traditional certificate;
generating a first post-quantum certificate with identical information fields as the first traditional certificate, wherein the first post-quantum certificate is bound to the first traditional certificate and performs a same purpose as the first traditional certificate;
populating a serial number field with a serial number of the first post-quantum certificate using the first digital fingerprint of the first traditional certificate to which the first post-quantum certificate is bound, wherein the first digital fingerprint is the serial number;
verifying the serial number of the first post-quantum certificate matches the first digital fingerprint of the first traditional certificate, wherein the first digital fingerprint acts as a validation indicator of binding between the first traditional certificate and the first post-quantum certificate;
detecting a vulnerable certificate in the certificate chain, wherein the vulnerable certificate contains an encryption algorithm susceptible to attack;
calculating a second digital fingerprint of the vulnerable certificate;
generating a second post-quantum certificate with identical information fields as the vulnerable certificate; and
populating a second serial number of the second post-quantum certificate using the second digital fingerprint.
|