| CPC G11C 11/4093 (2013.01) [G11C 8/18 (2013.01); G11C 11/4087 (2013.01); G11C 11/4096 (2013.01); H03K 19/1737 (2013.01); H03K 19/17728 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
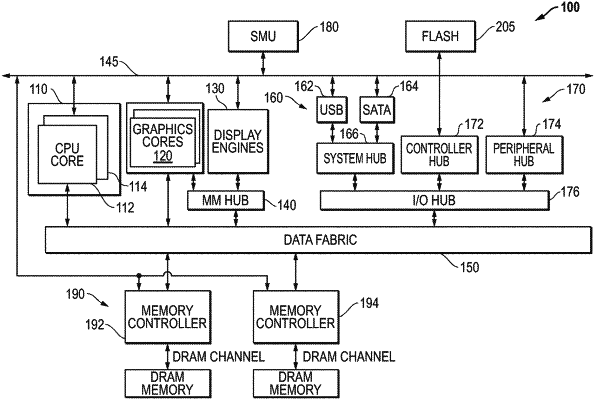
1. A fine-grained dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) comprising:
a first memory bank including a memory array divided into a plurality of grains, each grain including a row buffer and input/output (I/O) circuitry;
a second memory bank; and
a dual-mode I/O circuit coupled to the I/O circuitry of each grain in the first memory bank, the dual-mode I/O circuit operating in a first mode in which commands having a first data width are routed to and fulfilled individually at each grain, and a second mode in which commands having a second data width different from the first data width are fulfilled by at least two of the grains in parallel.
|