| CPC G06F 9/451 (2018.02) [G06F 8/34 (2013.01); G06F 11/3608 (2013.01); G06N 3/042 (2023.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06Q 30/0277 (2013.01); G07G 5/00 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method implemented using one or more processors, comprising:
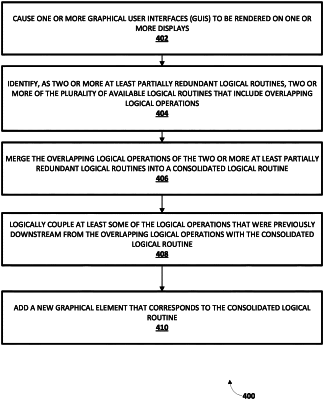
causing one or more graphical user interfaces (GUIs) to be rendered on one or more displays, wherein each GUI of the one or more GUIs includes a working canvas on which a plurality of graphical elements corresponding to at least some of a plurality of available logical routines are manipulable to define a machine learning state machine, and wherein one or more of the available logical routines includes logical operations that process data using one or more machine learning models;
identifying, as two or more at least partially redundant logical routines, two or more of the plurality of available logical routines that include overlapping logical operations;
merging the overlapping logical operations of the two or more at least partially redundant logical routines into a consolidated logical routine; and
logically coupling at least some of the logical operations that were previously downstream from the overlapping logical operations with the consolidated logical routine.
|