| CPC G05D 1/12 (2013.01) [B64C 39/024 (2013.01); B64D 47/08 (2013.01); G05D 1/0094 (2013.01); G05D 1/101 (2013.01); B64U 2101/30 (2023.01); B64U 2201/10 (2023.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
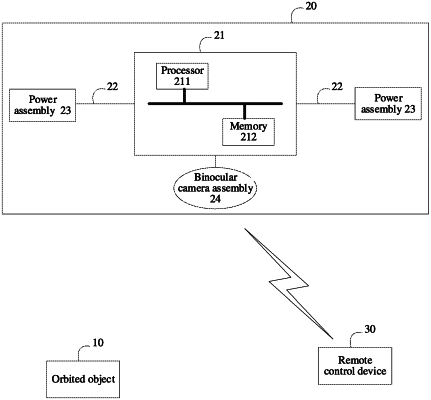
1. An autonomous orbiting method, applicable to an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), the UAV comprising a binocular camera assembly, the method comprising:
obtaining, through the binocular camera assembly, a target footage and an orbited object selected by a user from the target footage;
obtaining a flying height of the UAV when obtaining the target footage;
determining a spatial distance between the binocular camera assembly and the orbited object based on the target footage; wherein the target footage comprises a left camera view and a right camera view for the same shooting scene, and the step of determining a spatial distance between the binocular camera assembly and the orbited object comprises: obtaining a disparity value of the orbited object by stereo matching the left camera view and the right camera view, so as to obtain the spatial distance between the binocular camera assembly and the orbited object;
detecting an optical axis direction of the binocular camera assembly in real time; and
performing autonomous orbiting according to the flying height, the spatial distance and the optical axis direction of the binocular camera assembly detected in real time; using the flying height as a target flying height of the UAV; using the spatial distance as a target spatial distance between the binocular camera assembly and the orbited object; and maintaining the target flying height and the target spatial distance unchanged, and adjusting a flight direction of the UAV according to the optical axis direction of the binocular camera assembly detected in real time, to perform the autonomous orbiting centered on the orbited object.
|