| CPC G01N 27/125 (2013.01) [G01N 33/0006 (2013.01); G06N 3/044 (2023.01)] | 23 Claims |
|
1. A method, comprising:
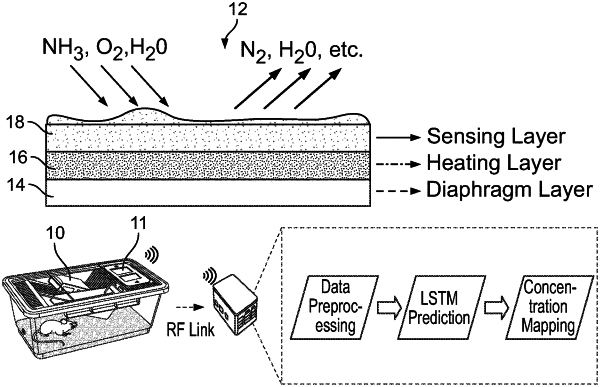
heating a metal oxide sensor for a predetermined period of time for the metal oxide sensor to interact with a surrounding gas, wherein the metal oxide sensor includes a heater;
sampling, during the heating, transient resistance values of the metal oxide sensor to obtain sampled transient resistance values;
determining an electrical resistance of the metal oxide sensor in a chemical equilibrium state of the interaction of the metal oxide sensor and the surrounding gas, wherein determining the equilibrium electrical resistance is based at least upon the sampled transient resistance values and via applying a neural network; and
determining a concentration level of the surrounding gas at the chemical equilibrium state by mapping the determined electrical resistance to a corresponding concentration level of the surrounding gas.
|