| CPC F28F 13/16 (2013.01) | 6 Claims |
|
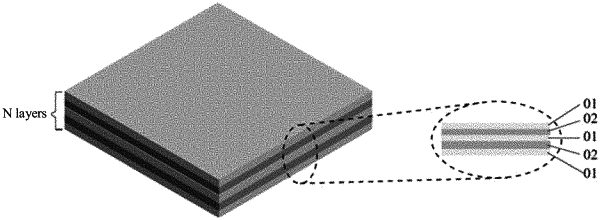
1. A visible light-transparent and radiative-cooling multilayer film comprising N layers of films, wherein the N layers of films comprise layers of first films and layers of second films arranged alternately;
wherein the layers of first films and the layers of second films are made of different visible light-transparent materials, and the visible light-transparent materials have different dielectric constants in infrared band, and a resonant cavity or resonant cavities are formed between the layers of first films and the layers of second films,
wherein the N layers of films have layers of materials with different thicknesses,
wherein each of the layers of first films has a thickness of d1, wherein 0.1 μm≤d1≤1 μm,
wherein each of the layers of second films has a thickness of d2, wherein 1 μm≤d2≤3 μm,
wherein the layers of first films are made of indium tin oxide, and the layers of second films are made of photoresist,
wherein the layers of first films include a thickest layer, the layers of second films include a least thick layer, the thickness of the thickest layer is less thick than the thickness of the least thick layer.
|