| CPC F24D 19/1033 (2013.01) [F24D 3/02 (2013.01); F24D 19/0012 (2013.01); G05B 19/042 (2013.01); F24D 2220/0235 (2013.01); F24D 2220/042 (2013.01); G05B 2219/2614 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
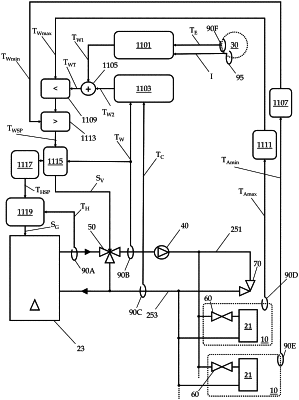
1. A system for heating a building comprising:
a heat generator to heat a carrier fluid,
at least one radiating element for transferring heat to a thermal load included in a building,
a delivery conduit for transferring the carrier fluid from the heat generator to the radiating element,
a return conduit for transferring the carrier fluid from the radiating element to the heat generator,
a three-way valve arranged along the delivery conduit and connected to the return conduit, the three-way valve operable to mix the carrier fluid in the delivery conduit to the carrier fluid in the return conduit,
a plurality of temperature sensors arranged to measure the temperature of the carrier fluid and a temperature of the environment outside the building, and
a control unit operatively connected to the heat generator, the three-way valve and the temperature sensors,
wherein the control unit is configured for:
a) acquiring a temperature of the carrier fluid in the delivery conduit downstream of the three-way valve with respect to the direction of the flow of the carrier fluid in the delivery conduit,
b) acquiring a temperature of the carrier fluid in the return conduit upstream of the three-way valve with respect to the direction of the flow of the carrier fluid in the return conduit,
c) acquiring a temperature of the environment outside the building,
d) estimating a first target temperature of the carrier fluid in the delivery conduit downstream of the three-way valve, based on a simplified model of the system calculated as a function of the temperature of the external environment,
e) actuating at least one among the heat generator and the three-way valve to generate a periodic perturbation in the temperature of the carrier fluid downstream of the three-way valve,
f) determining a second target temperature of the carrier fluid in the delivery conduit downstream of the three-way valve based on a temperature difference between the temperature of the carrier fluid in the delivery conduit and the temperature of the carrier fluid in the return conduit based on said perturbation,
g) combining the first target temperature and the second target temperature to obtain a total target temperature,
h) actuating at least one among the heat generator and the three-way valve to bring the carrier fluid in the delivery conduit downstream of the three-way valve to the total target temperature, and
i) reiterating steps e) to h) until reaching a target temperature difference between the temperature of the carrier fluid in the delivery conduit and the temperature of the carrier fluid in the return conduit.
|