| CPC B60W 60/0027 (2020.02) [G05D 1/0214 (2013.01); B60W 2554/00 (2020.02); G01S 13/931 (2013.01); G01S 2013/9323 (2020.01); G01S 2013/9324 (2020.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A vehicle comprising:
a time-of-flight sensor;
one or more processors; and
memory storing processor-executable instructions that, when executed by the one or more processors, configure the vehicle to perform actions comprising:
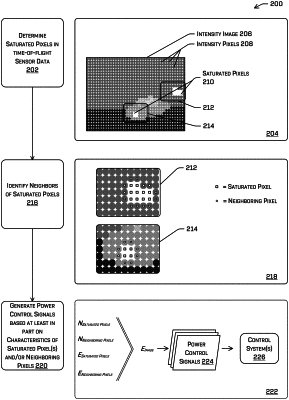
receiving sensor data from the time-of-flight sensor, the sensor data comprising a plurality of phase frames comprising phase values for a plurality of pixels;
determining, based at least in part on the phase values for the plurality of pixels, saturated pixels of the plurality of pixels;
determining neighboring pixels of the plurality of pixels, the neighboring pixels being non-saturated pixels adjacent at least one of the saturated pixels;
determining an energy metric associated with the sensor data, the energy metric being based at least in part on one or characteristics of the neighboring pixels;
generating, based at least in part on the energy metric, a signal to alter at least one of an illumination intensity or an integration time associated with the time-of-flight sensor; and
sending the signal to the time-of-flight sensor.
|