| CPC A61B 5/7282 (2013.01) [A61B 5/7475 (2013.01); A61B 7/003 (2013.01); A61B 5/4818 (2013.01); A61B 5/6803 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method, automatically implemented by one or more processors of a computing device, for automatically characterizing recorded digital breath sounds acquired from a candidate while sleeping, as potentially indicative of an obstructive breathing disorder, the method comprising:
receiving, at the at least one processor, the recorded digital breath sounds of an upper airway of the candidate;
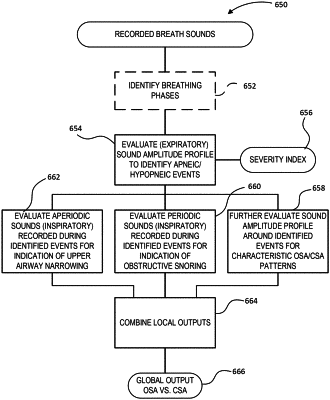
automatically identifying inspiration and expiration phases of said recorded digital breath sounds;
automatically identifying, by the at least one processor, periodic breath sound segments and aperiodic breath sound segments from the recorded digital breath sounds;
automatically identifying at least one apnea or hypopnea from the expiration phases of the recorded digital breath sounds;
based on the identified apnea or hypopnea, automatically selecting one or more of said aperiodic breath sound segments so to encompass corresponding ones of said at least one apnea or hypopnea, and to classify the said at least one apnea or hypopnea as being associated with a central sleep apnea versus an obstructive sleep apnea;
extracting from the identified periodic breath sound segments, by the at least one processor, one or more periodic breath sound characteristics;
evaluating, by the at least one processor, the extracted periodic breath sound characteristics against one or more corresponding periodic breath sound classification criteria predetermined to distinguish obstructive periodic breathing events from non-obstructive periodic breathing events;
extracting from inspiration phase of the selected aperiodic breath sound segments, by the at least one processor, one or more aperiodic breath sound characteristics comprising one or more upper airway narrowing characteristics;
evaluating, by the at least one processor, the extracted aperiodic breath sound characteristics against one or more corresponding aperiodic breath sound classification criteria predetermined to distinguish obstructive aperiodic breathing events from non-obstructive aperiodic breathing events;
identifying, by the at least one processor, a time-domain breath sound amplitude profile segment of the recorded digital breath sounds encompassing said at least one of an apnea and a hypopnea;
evaluating, by the at least one processor, the time-domain breath sound amplitude profile segment against one or more preset time-domain sound amplitude profile criteria set to recognize a profile pattern indicative of said obstructive apnea;
combining, by the at least one processor, results of the three evaluating steps to provide an indication as to whether the candidate likely suffers from the obstructive breathing disorder, the indication generated based upon a classifier, the classifier receiving results of the three evaluating steps as inputs, and
outputting the indication using a display device in communication with the at least one processor.
|