| CPC A61B 5/4094 (2013.01) [A61B 5/7267 (2013.01); G06T 7/00 (2013.01); G06T 7/20 (2013.01); G06T 7/70 (2017.01); G16H 50/70 (2018.01)] | 17 Claims |
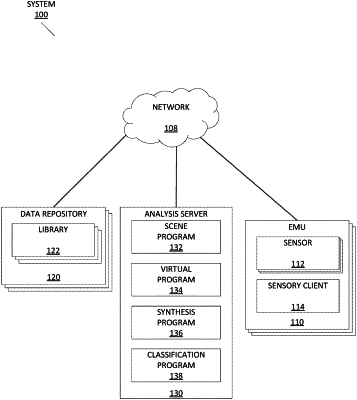
|
1. A computer-implemented method for determining abnormal motion from a patient, the method comprising:
receiving sensory data of the patient and a location in which the patient is present, the sensory data including video data over a period of time the patient is being monitored;
generating contextual information based on the sensory data, the contextual information indicative of surroundings of the patient and characteristics of the location;
generating motion information based on the sensory data, the motion information indicative of movement of the patient in the location;
generating contextual motion data; and
determining the abnormal motion based on the contextual motion data,
wherein the contextual motion data is generated by generating a virtual environment based on the contextual information;
generating a model actor representing the patient;
generating a simulation of the movement of the patient via the model actor in the virtual environment; and
processing the simulation.
|