| CPC H05B 45/347 (2020.01) [H05B 45/3725 (2020.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
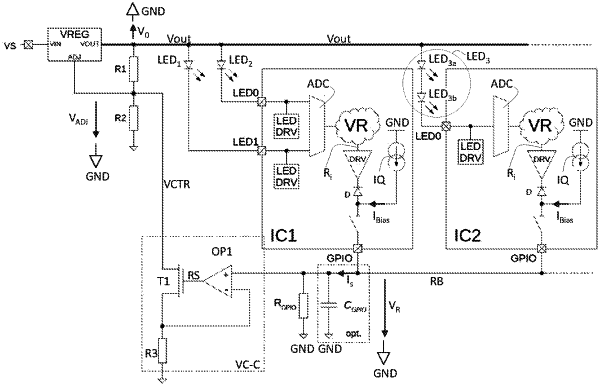
1. A method for regulating an output voltage at an output of a current-controlled voltage regulator for supplying a lighting device with electrical energy, wherein the lighting device includes at least two circuits, the at least two circuits including a first circuit and a second circuit,
wherein each of the at least two circuits is constructed to supply more than one LED group with electrical energy by a current source associated with the LED group, and
wherein the current source is a LED driver,
the method comprising:
generating the output voltage by the current-controlled voltage regulator at the output;
supplying the LEDs of the LED groups using the output voltage;
setting of a first LED group current through the more than one LED group by the current source of the first circuit associated with the respective LED group of the first circuit;
setting of a second LED group current through the at least one LED group by the current source of the second circuit associated with the respective LED group of the second circuit;
if necessary, setting of a third LED group current through an at least one further LED group by the current source of a further circuit associated with this further LED group;
detecting respective voltage drops across the respective of the LED groups as respective voltage drop values of the current source within the respective circuits, wherein a separate voltage drop value is detected for each current source;
selecting the respective voltage drop value of one of the respective current sources of each circuit from the voltage drop values of the current sources of the respective circuit as a characteristic voltage drop value of the circuit;
withdrawing of a respective withdrawal current of the respective circuit from a control bus by each of the at least two circuits, wherein:
an amount of the respective withdrawal current of the respective circuit depends on a deviation of its characteristic voltage drop value from a set value, and
all of the withdrawal currents and at least one optional constant bias current are summed to a total current, and
regulating the output voltage of the current-controlled voltage regulator at its output as a function of the sum current;
wherein:
the amount of the respective withdrawal current of the respective circuit depends linearly on a deviation of its characteristic voltage drop value from a set value, and
the current-controlled voltage regulator is current controlled.
|