| CPC H04S 7/40 (2013.01) [H04S 7/303 (2013.01); H04S 2420/01 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
spatializing a sound source for an initial position in a local area using an initial version of a head-related transfer function (HRTF) to obtain an initial spatialized sound source;
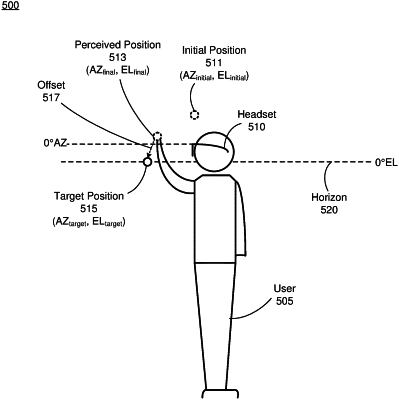
upon presenting the initial spatialized sound source to a user, adjusting, in an iterative manner based on at least one perceptive response from the user, at least one property of the HRTF to generate a version of the HRTF customized for the user, each perceptive response from the user indicating a respective offset between a perceived position and a target position of the sound source upon presentation of at least one spatialized version of the sound source, wherein adjusting the at least one property of the HRTF comprises:
pointing, by the user via an interface device, to at least one location in the local area as at least one perceived location of the sound source, the at least one location being outside of a field of view of the user, and
extrapolating, based on the at least one pointed location and using a machine learning (ML) model, one or more parameters associated with the HRTF to generate the customized version of the HRTF;
applying the customized version of the HRTF to one or more audio channels to form spatialized audio content for the perceived position; and
presenting the spatialized audio content to the user, wherein the offset between the perceived position and the target position is reduced.
|