| CPC H04R 25/45 (2013.01) [G10L 15/20 (2013.01); H04R 2225/43 (2013.01)] | 23 Claims |
|
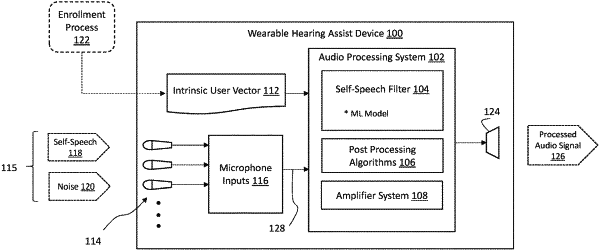
1. A method of removing user speech for a hearing assist device, comprising:
receiving an audio signal, wherein the audio signal includes a speech component of the user and a noise component;
filtering the audio signal with a self-speech filter that utilizes an intrinsic user vector stored with the self-speech filter to filter the speech component, wherein the intrinsic user vector is created offline prior to receiving the audio signal based on a voice input of the user; and
outputting a filtered audio signal in which the speech component of the user has been substantially removed from the audio signal.
|
|
12. A system, comprising:
a memory; and
a processor coupled to the memory and configured to remove user speech for a hearing assist device according to a method that comprises:
receiving an audio signal, wherein the audio signal includes a speech component of the user and a noise component;
filtering the audio signal with a self-speech filter that utilizes an intrinsic user vector to filter out the speech component, wherein the intrinsic user vector is determined offline based on a voice input of the user and is stored with the self-speech filter; and
outputting a filtered audio signal in which the speech component of the user has been substantially removed from the audio signal.
|
|
23. A system, comprising:
a memory; and
a processor coupled to the memory and configured to perform a method that comprises:
receiving an audio signal, wherein the audio signal includes a targeted speech component of a non-device user and a noise component;
filtering the audio signal with a targeted speech enhancer that utilizes an intrinsic user vector to substantially pass only the targeted speech component, wherein the intrinsic user vector is determined based on a voice input of the non-device user; and
outputting a speech enhanced audio signal substantially containing only the targeted speech component.
|