| CPC H04B 10/27 (2013.01) [H04L 1/004 (2013.01); H04L 7/0075 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
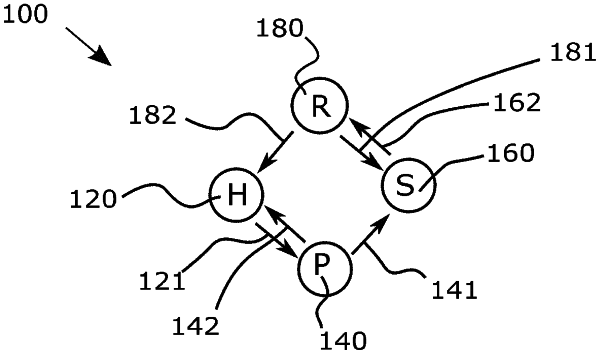
1. A circuit for a passive optical network (PON) comprising:
one or more processors configured to:
operate in a hunt state, wherein the one or more processors is configured to detect frame boundaries associated with an incoming data signal based on detecting a predefined synchronization (psync) pattern associated with a set of hunt frames comprising one or more consecutive frames associated with the incoming data signal;
transition to a pre-sync state if the predefined psync pattern is detected correctly for at least one frame of the set of hunt frames; and
operate in the pre-sync state, wherein the one or more processors is configured to perform forward error correction (FEC) decoding on a payload data portion of a set of pre-sync frames comprising one or more subsequent consecutive frames associated with the incoming data signal and detect a loss of synchronization in the pre-sync state based on the FEC decoding on the payload data portion.
|