| CPC H02K 5/132 (2013.01) [E21B 43/128 (2013.01); F04B 49/06 (2013.01); F04C 13/008 (2013.01); F04D 15/0066 (2013.01); H02P 6/08 (2013.01); H02P 25/022 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
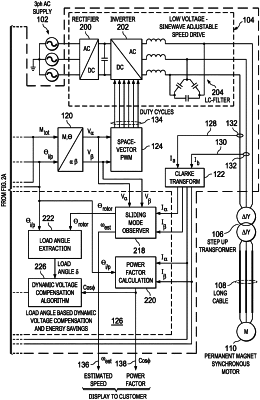
1. A method for controlling a permanent magnet (PM) synchronous motor, comprising:
estimating a load angle of the PM motor by:
estimating a rotor angle of the PM motor, wherein the rotor angle corresponds to an induced electromagnetic field (EMF) within the PM motor;
obtaining an open loop reference angle of the PM motor, wherein the reference angle corresponds to a terminal voltage of the PM motor; and
calculating the load angle as a difference between the open loop reference angle and the rotor angle;
determining a voltage adjustment value for the PM motor based at least on the estimated load angle of the PM motor; and
determining a voltage to be applied to the PM motor based on the voltage adjustment value.
|