| CPC G10L 15/26 (2013.01) [G06F 3/167 (2013.01); G10L 15/183 (2013.01); G10L 15/1815 (2013.01); G10L 15/22 (2013.01); G10L 15/30 (2013.01); G10L 2015/223 (2013.01)] | 24 Claims |
|
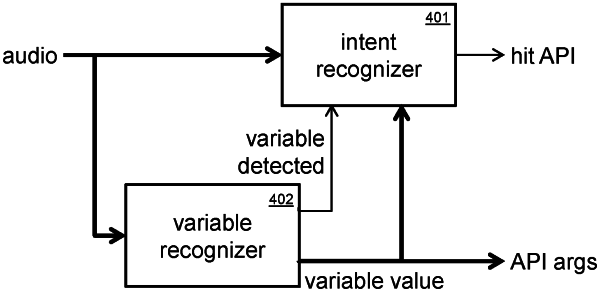
1. A machine for recognizing an intent in speech audio, the machine comprising:
a variable recognizer that processes speech audio features, computes a probability of the speech audio having any of a plurality of enumerated variable values, and outputs the value of the plurality of enumerated variable values with the highest probability; and
an intent recognizer that processes speech audio features, computes a probability of the speech audio having the intent, and in response to the probability being above an intent threshold, produces a request for a virtual assistant action,
wherein the machine has no lexical representation of the speech audio;
the variable recognizer indicates the probability of the speech audio having a value from the plurality of enumerated variable values;
the intent recognizer conditions its output of a request for an action on the probability of the speech audio having a value from the plurality of enumerated variable values; and
the conditioning is based on a delayed indication of the probability of the speech audio having a value from the plurality of enumerated variable values.
|