| CPC G06T 5/30 (2013.01) [G01C 21/3415 (2013.01); G06T 7/90 (2017.01); G08G 1/0133 (2013.01); G08G 1/0141 (2013.01); G08G 1/0145 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A system, comprising:
at least one storage medium including a set of instructions for identifying one or more target roads; and
at least one processor in communication with the at least one storage medium, wherein when executing the set of instructions, the at least one processor is directed to:
obtain position information associated with a plurality of vehicles through a plurality of positioning devices of the plurality of vehicles in a target region;
obtain, based on the position information associated with the plurality of vehicles, a heat map associated with a plurality of driving track points of the plurality of vehicles along a plurality of roads in the target region, wherein the plurality of roads includes one or more target roads and one or more reference roads;
obtain a road network map associated with the one or more reference roads in the target region;
produce an intermediate heat map by:
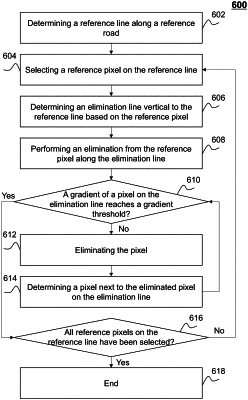
eliminating pixels in the heat map corresponding to the one or more reference roads in the road network map by:
identifying an intersection between a first group of pixels corresponding to a first group of driving track points and a second group of pixels corresponding to a second group of driving track points in the heat map;
performing a first elimination of pixels along a first reference line associated with the first group of pixels based on a gradient threshold;
performing a second elimination of pixels along a second reference line associated with the second group of pixels based on the gradient threshold; and
determining a target elimination result based on an overlapping result of the first elimination and the second elimination; and
eliminating background pixels corresponding to background of the heat map; and
conducting an image thinning operation to the heat map; and
determine start coordinate information and end coordinate information associated with the one or more target roads based on the intermediate heat map according to a linear transformation.
|