| CPC G06N 3/084 (2013.01) [G06F 17/16 (2013.01); G06N 3/049 (2013.01); G06N 3/08 (2013.01); G06N 3/088 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
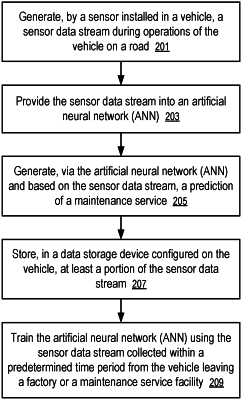
1. A data storage device of a vehicle, comprising:
a hardware host interface configured to receive a sensor data stream from at least one sensor configured on the vehicle;
at least one storage media component having a non-volatile memory configured to store at least a portion of the sensor data stream;
a controller; and
a neural network accelerator coupled to the controller, the neural network accelerator configured to:
determine whether a first portion of the sensor data stream is obtained during a time period during which the vehicle is expected to operate in a normal mode;
pre-classify the first portion of the sensor data stream obtained during the time period as normal and into a plurality of clusters corresponding to different types of normal operating conditions associated with the vehicle;
perform at least a portion of computations utilizing an artificial neural network to predict a time for a maintenance service of the vehicle based on the first portion of the sensor data stream;
detect an anomaly associated with a component of the vehicle based on a second portion of the sensor data being classified outside the plurality of clusters;
estimate a degree of severity for the anomaly associated with the component of the vehicle to facilitate scheduling of the maintenance service; and
adjust the artificial neural network by training the artificial neural network based on the sensor data stream and an actual time for the maintenance service of the vehicle to reduce a difference between a predicted time for a future maintenance service and an actual time for the future maintenance service, wherein the artificial neural network is trained during the time period during which the vehicle is expected to operate in the normal mode.
|