| CPC G02B 6/0036 (2013.01) [G02B 30/27 (2020.01); G02B 30/33 (2020.01); G02B 30/35 (2020.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
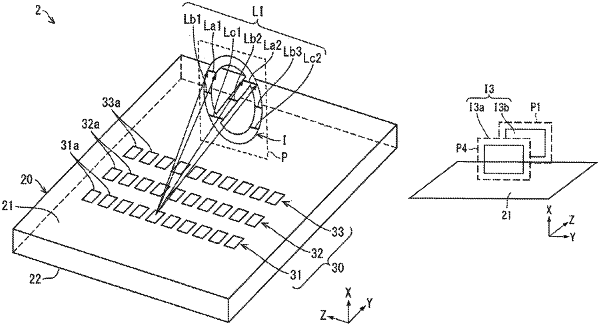
1. A display method for a stereoscopic image, using a display device provided with a transparent optical element, wherein the transparent optical element comprises an incident surface for a light from a light source to enter into the transparent optical element; a rear surface totally reflecting the light entered from the incident surface; an optical path changing unit disposed on the rear surface, the optical path changing unit changing an optical path of the light guided in the transparent optical element; and an outgoing surface emitting the light guided inside the transparent optical element and changed in the optical path by the optical path changing unit, the display method comprising:
emitting the light to be recognized by an observer as a stereoscopic image from the transparent optical element; and
displaying at least a part of the stereoscopic image on a plane not parallel to the outgoing surface of the transparent optical element,
wherein the observer is able to visually recognize a rear surface side of the display device through the transparent optical element,
wherein the stereoscopic image has two planes positioned on mutually different planes,
wherein the two planes are parallel to each other, identical in shape, and identical in size,
wherein when viewed in a direction perpendicular to the two planes, the two planes do not completely overlap each other, and
wherein the optical path changing unit includes: a first optical path changing unit for image formation of a first plane which is one of the two planes; and a second optical path changing unit for image formation of a second plane which is the other of the two planes.
|