| CPC D01F 6/625 (2013.01) [A61L 27/18 (2013.01); A61L 29/06 (2013.01); A61L 31/06 (2013.01); D02J 1/20 (2013.01); D10B 2331/041 (2013.01); D10B 2401/061 (2013.01); D10B 2509/00 (2013.01)] | 32 Claims |
|
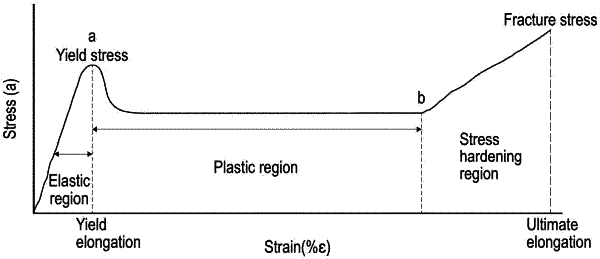
1. A melt extruded, oriented polymeric material fiber, wherein the polymeric material is a homopolymer of caprolactone or a copolymer of at least 90% by weight of caprolactone and one or more additional monomers; and further wherein:
(i) the polymeric material fiber has a tensile strength of about 450 MPa to about 650 MPa; and/or
(ii) the polymeric material fiber has an elongation at break in the range of 45% to 65%; and/or
(iii) the polymeric material fiber has an elastic modulus in the range of 750 MPa to 1200 MPa; and/or
(iv) the tensile strength of the polymeric material fiber, as measured after immersion in phosphate buffered physiological saline for 60 minutes, decreases less than 20% after immersion in phosphate buffered physiological saline for 6 months.
|