| CPC C11D 3/0078 (2013.01) [C08F 230/02 (2013.01); C08L 43/02 (2013.01); G02C 7/04 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
1. A soft contact lens treatment method, comprising subjecting a soft contact lens to surface treatment with a treating solution containing a copolymer (P) consisting of a combination of 50 mol % to 99 mol % of a hydrophilic monomer represented by the formula (1a) and 1 mol % to 50 mol % of 2-aminoethyl methacrylate hydrochloride, and that has a weight-average molecular weight of from 10,000 to 5,000,000:
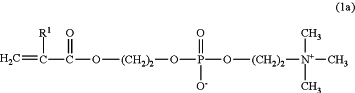 in the formula (1a), R1 represents a hydrogen atom or a methyl group.
|