| CPC A61N 5/1031 (2013.01) [A61K 51/0497 (2013.01); A61M 37/0092 (2013.01); A61N 2005/1098 (2013.01)] | 23 Claims |
|
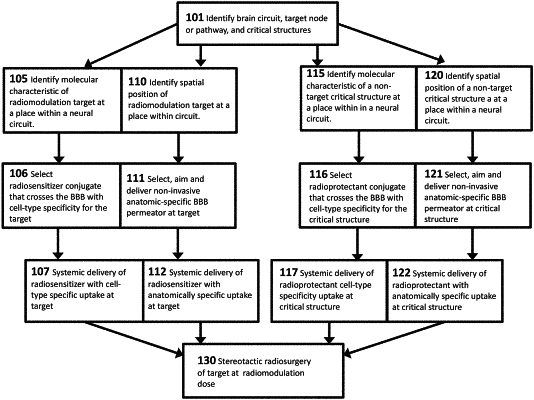
10. A treatment system for treatment of a disorder of a brain of a patient, the treatment system comprising:
a first substance having a specific cell-type affinity for certain types of brain cells, wherein the first substance has properties that enhance radiation effects at a targeted tissue associated with a neural circuit contributing to the disorder and/or inhibit irradiation of non-targeted tissues of critical structures of the brain, wherein the first substance includes a conjugate of a first molecular structure having the affinity for the certain types of cells and a second molecular structure includes either a radiosensitizer or a radioprotectant; and
a blood-brain barrier permeator configured to permeate a blood-brain barrier of the brain upon delivery to the blood-brain barrier;
a second substance including a third molecular structure and a fourth molecular structure, the third molecular structure having a specific cell-type affinity for a second type of brain cells of the critical structures of the brain that are not the target of the radiotherapy, and the fourth molecular structure having the radioprotectant to protect the non-targeted tissues of the critical structures of the brain during the radiotherapy; and
a radiation delivery system configured to deliver radiation to the targeted tissue at a therapeutically effective dose;
wherein the radiation of the targeted tissue is enhanced by the presence of the first substance if the second molecular structure includes the radiosensitizer and wherein undesired alteration of the non-targeted tissues of the critical structures of the brain is avoided if the second molecular structure includes the radioprotectant;
wherein the first molecular structure has the specific cell-type affinity for a first type of brain cells being targeted for radiotherapy and the second molecular structure includes the radiosensitizer configured to enhance the radiation of the first type of brain cells.
|