| CPC A61B 90/361 (2016.02) [A61B 1/0005 (2013.01); A61B 1/00194 (2022.02); A61B 1/045 (2013.01); A61B 1/05 (2013.01); A61B 1/0605 (2022.02); A61B 1/0638 (2013.01); G06T 7/0012 (2013.01); A61B 1/000094 (2022.02); G06T 2207/10068 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20221 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30004 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
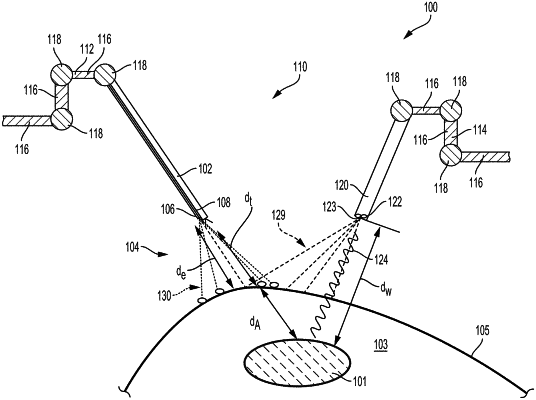
1. A surgical imaging system comprising:
a multispectral electromagnetic radiation (EMR) source configured to emit EMR at a first wavelength range and a second wavelength range;
an image sensor configured to sense the EMR at each of the first wavelength range and the second wavelength range reflected from a target site; and
a control circuit coupled to the image sensor, the control circuit configured to:
generate a first image of the target site of a subsurface structure according to the EMR emitted at the first wavelength range;
determine whether the first image is at least partially obstructed by an obscurant, wherein the obscurant obstructs the view of the subsurface structure;
select the second wavelength range to minimize absorption by the obscurant;
generate a second image of the target site according to the EMR emitted at the second wavelength range; and
generate a fused image comprising a fusion between an unobstructed segment of the first image at the first wavelength range and a segment of the second image corresponding to an obstructed segment of the first image at the second wavelength range.
|