| CPC A61B 5/4094 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0205 (2013.01); A61B 5/316 (2021.01); A61B 5/352 (2021.01); A61B 5/374 (2021.01); A61B 5/7275 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. A method of evaluating the effectiveness of an intervention measure, comprising:
estimating the risk of occurrence of a physiological event in a mammal, wherein said estimating comprises:
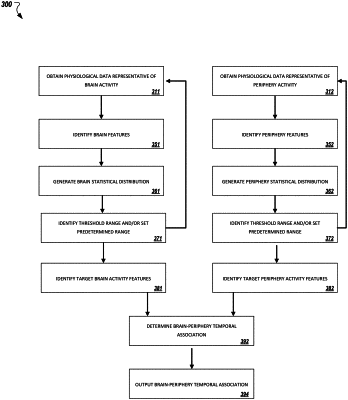
obtaining brain activity data that describes brain activity of the mammal over a first period of time;
obtaining peripheral activity data that describes peripheral activity of the mammal over a second period of time;
receiving, by at least one device, brain data from a brain activity measurement device that describes brain activity of a mammal over the first period of time;
receiving, by the at least one device, periphery data from a peripheral activity measurement device that describes peripheral activity of a mammal over the second period of time;
generating, by the at least one device, one or more brain feature representations based on the brain data;
generating, by the at least one device, one or more periphery feature representations based on the periphery data;
generating, by the at least one device, one or more brain statistical distributions of the one or more brain feature representations;
generating, by the at least one device, one or more periphery statistical distributions of the one or more periphery feature representations;
identifying, by the at least one device, one or more brain feature representations that fall outside of a predetermined range in the brain statistical distribution to generate a set of one or more target brain feature representations;
identifying, by the at least one device, one or more periphery feature representations that fall outside of a predetermined range in the periphery statistical distribution to generate a set of one or more target periphery feature representations;
determining, by the at least one device, a brain-periphery temporal association between the one or more target brain feature representations and the one or more target periphery feature representations;
determining, by the at least one device, an estimate of risk of a future physiological event based on the brain-periphery temporal association; and
providing, by the at least one device, an indication of the estimate of risk of the future physiological event;
applying at least one intervention measure that is commensurate with the prevention of the physiological event; and
determining the effectiveness of the intervention measure.
|