| CPC G16C 20/10 (2019.02) [G06F 16/90335 (2019.01); G06N 5/025 (2013.01); G06F 17/13 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
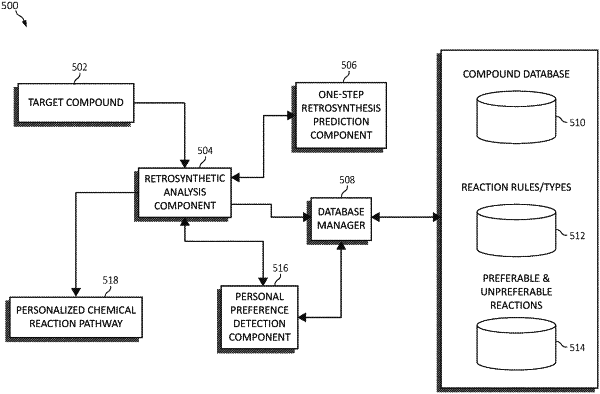
|
1. A method for intelligent discovery of preferred chemical reaction pathways to a synthesized target compound in a computing environment by a processor, comprising:
receiving, by the processor, target compound data of a target compound a user intends to synthesize;
calculating, by the processor using at least one of a node graph searching operation and a machine learning operation, a preference score for one or more chemical reaction pathways to the target compound based on one or more chemical reactions, wherein the preference score is personalized to a skill level of the user and calculated based on detected preferences of the user, the detected preferences inclusive of starting materials and equipment available to the user to synthesize the target compound;
determining, by the processor as an output of the at least one of the node graph searching operation and the machine learning operation, one or more preferred chemical reaction pathways to synthesize the target compound using a modified retrosynthetic analysis according to the preference score for one or more chemical reactions, wherein, given input of the target compound, the determination of precursor compounds of the one or more preferred chemical reaction pathways to synthesize the target compound are returned as the output in one reaction step; and
displaying, by the processor via an interactive graphical user interface (GUI), the one or more preferred chemical reaction pathways to the target compound listed in an order based on the preference score for the one or more chemical reactions.
|