| CPC H04N 19/103 (2014.11) [H04N 19/136 (2014.11); H04N 19/184 (2014.11)] | 8 Claims |
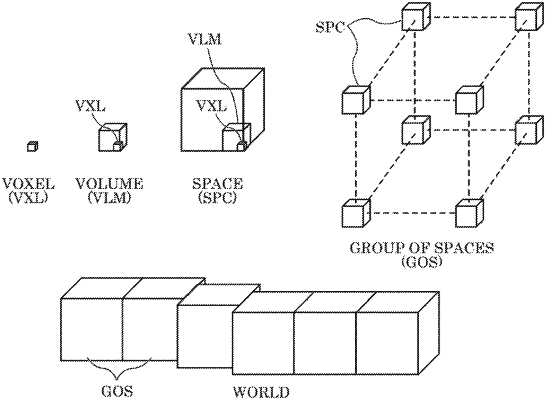
|
1. A three-dimensional data encoding method of encoding three-dimensional points, the three-dimensional data encoding method comprising:
calculating a predicted value, using attribute information of one or more second three-dimensional points, according to a first method when a third three-dimensional point included in the one or more second three-dimensional points is spatially coincident with a first three-dimensional point, the predicted value being used for calculating attribute information of the first three-dimensional point;
calculating the predicted value, using the attribute information of the one or more second three-dimensional points, according to a second method that is different from the first method when the third three-dimensional point is not spatially coincident with the first three-dimensional point;
calculating a prediction residual which is a difference between the attribute information of the first three-dimensional point and the predicted value; and
generating a bitstream including the prediction residual.
|