| CPC G16H 50/20 (2018.01) [A61B 5/165 (2013.01); G06Q 10/06316 (2013.01); G16H 40/20 (2018.01); G16H 40/67 (2018.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01); G16H 70/20 (2018.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
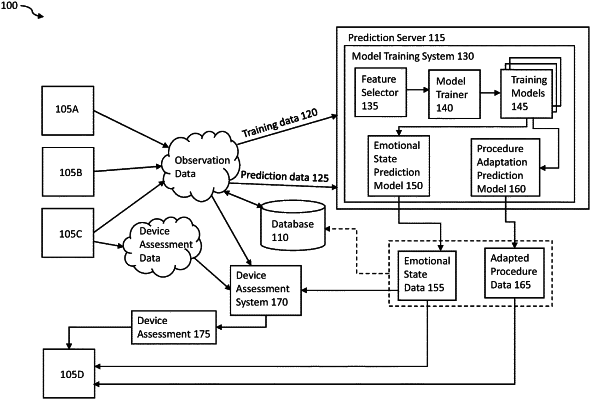
training a predictive model configured on a first computing system to determine adaptations of a clinical procedure performed by a medical professional in an operating room using an instrument, the predictive model trained using observation data associated with the medical professional performing the clinical procedure using the instrument, the observation data including image data acquired via a camera sensor configured within the operating room and having a field of view of the medical professional's hands and face, the observation data further including instrument data acquired via an instrument sensor configured in the instrument;
configuring a trained predictive model on a second computing system configured in an operating room configured with a camera sensor in which a first medical professional is performing a clinical procedure, the trained predictive model corresponding to the predictive model trained on the first computing system;
receiving, by the trained predictive model, observation data associated with the medical professional performing the clinical procedure in the operating room using an instrument, the observation data including instrument data acquired by an instrument sensor configured within the instrument held by the medical professional during the clinical procedure and image data acquired by the camera sensor having a field of view including the instrument and the medical professional's hands and face, the instrument sensor and the camera sensor communicatively coupled to the second computing system;
determining, by the trained predictive model, at least one adaptation of the clinical procedure based on the received observation data, the at least one adaptation including training materials identifying a preference of the medical professional observed during the clinical procedure;
providing, by the second computing system, the at least one adaptation on a display of the second computing system, the at least one adaptation provided as ghost images acquired during previous instances of the clinical procedure performed by the medical professional, the ghost images overlaid atop camera data acquired as the medical professional performs the clinical procedure.
|