| CPC G06T 7/0014 (2013.01) [G06T 5/002 (2013.01); G06T 5/005 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20084 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30052 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
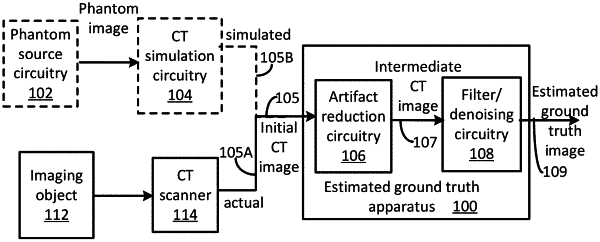
1. A method for computed tomography (CT) artifact reduction, the method comprising:
receiving, by an estimated ground truth apparatus, an initial CT image, the initial CT image comprising a major artifact;
generating, by an artifact reduction circuitry, an intermediate CT image based, at least in part, on the initial CT image, the intermediate CT image comprising a reduced artifact; and
generating, by the estimated ground truth apparatus, an estimated ground truth image based, at least in part, on the intermediate CT image, the estimated ground truth image to be used for training an artificial neural network,
adding, by a feature addition circuitry, a respective feature to each of a number, N, copies of the estimated ground truth image to create the number, N, initial training images;
generating, by a CT simulation circuitry, a plurality of simulated training CT images based, at least in part, on at least some of the N initial training images, each of at least some of the plurality of simulated training CT images containing at least one respective simulated artifact; and
training, by a convolutional neural network (CNN) training circuitry, a CNN based, at least in part, on the simulated training CT images and based, at least in part, on the initial training images.
|