| CPC G06T 7/0012 (2013.01) [A61B 3/102 (2013.01); G06T 7/12 (2017.01); G06T 7/143 (2017.01); G06T 7/149 (2017.01); G06T 7/168 (2017.01); G06T 2207/10101 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20064 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20121 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20124 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30041 (2013.01)] | 25 Claims |
|
1. A retinal OCT segmentation algorithm for segmenting a test retinal OCT image into 13 retinal regions, the algorithm comprising:
(a) providing a probabilistic shape and intensity model derived from a plurality of OCT images generated from control subjects and segmented into 13 retinal regions;
(b) aligning the test OCT image with the probabilistic shape and intensity model according to retinal region shape;
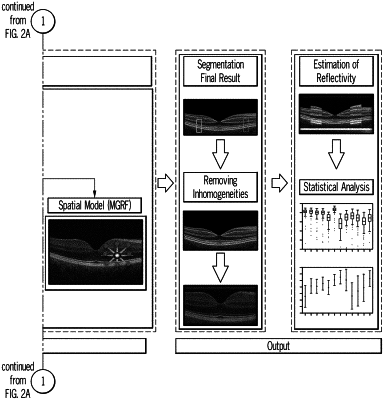
(c) comparing pixels of the aligned test OCT image with the corresponding pixels in the control model by intensity, establishing a probable regional fit, and refining regional margins by estimating marginal density distribution with a linear combination a linear combination of discrete Gaussians (LCDG) to generate an initial regional segmentation map of the test OCT image comprising defined retinal regions; and
(d) fitting the initial segmentation map with a statistical model that accounts for spatial information to achieve a final segmentation map comprising 13 retinal regions.
|