| CPC G06T 7/0004 (2013.01) [G06T 1/20 (2013.01); G06T 7/001 (2013.01); G06V 10/809 (2022.01); G06V 10/82 (2022.01); G06V 30/19113 (2022.01); G06V 30/248 (2022.01); G06T 2207/10116 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20084 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
|
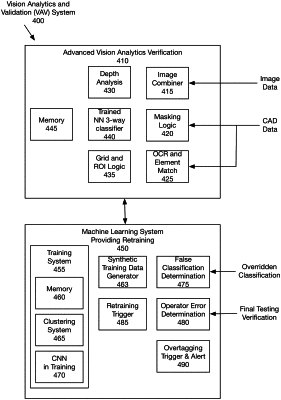
1. A vision analytics and validation (VAV) system for providing an improved inspection of robotic assembly system comprising:
an image combiner to combine a plurality of images from one or more camera-based inspection machines, the image combiner to create a unified image of a board;
a grid and ROI logic to create a grid aligned with the board, and to divide the unified image into regions of interest including an element and associated pads;
a processor implementing a trained neural network three-way classifier, to classify each component as good, bad, or do not know using the regions of interest;
an operator station configured to enable an operator to review an output of the trained neural network, and to determine whether a board including one or more “bad” or a “do not know” classified components passes review and is classified as good, or fails review and is classified as bad; and
a retraining trigger to add the output of the operator station to training data to train the trained neural network, when the determination received from the operator station does not match the classification of the trained neural network three-way classifier.
|