| CPC G06F 16/2465 (2019.01) [G05B 17/02 (2013.01); G06F 16/2272 (2019.01); G06F 16/2477 (2019.01); G06F 16/287 (2019.01); G06F 17/15 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
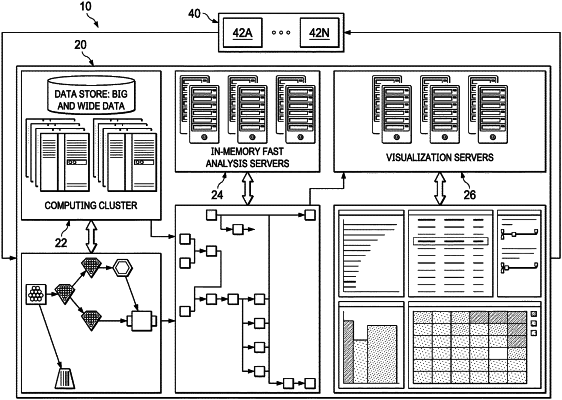
1. A process control tool for processing wide data from automated manufacturing operations, the process control tool comprising:
a feature selector configured to:
receive process input data from at least one manufacturing process application, wherein the process input data includes a plurality of observations and associated variables;
convert identified categorical variables into numerical variables and identified time-series data into fixed numbers of intervals; and
an analysis server configured to:
perform at least one operation to identify interactions between predictor values;
receive a subset of the predictor values; and
perform at least one of a statistical and modeling operation and pre-defined searches to identify interactions between the predictor values in the subset; and
a visualization engine configured to display the interactions for use in managing the manufacturing operations;
wherein the categorical variables are converted into the numerical variables by randomly dividing the categorical variables into two random samples, separately and individually computing an average for each category in each categorical variable, and replacing the categorical variables in each random sample with a computed average for the categorical variables in the other random sample;
wherein the categorial variables are discrete variables and the numerical variables are continuous variables.
|