| CPC G02C 7/066 (2013.01) [G02C 7/027 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
1. A progressive addition lens comprising:
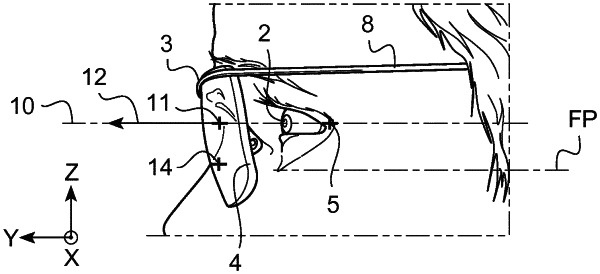
a first fitting point and a near vision reference point located on a same face of the lens, the first fitting point having an optical spherical power suitable for far vision in day light conditions, the first fitting point being positioned on a straight horizontal eye gaze direction when a user wears the progressive addition lens mounted in a frame with a null user head declination angle, the near vision reference point being positioned on a downward eye gaze direction when the user wears the progressive addition lens mounted in the frame with the null user head declination angle, the progressive addition lens comprising a first optical spherical power variation between the first fitting point and the near vision reference point; and
a second fitting point and a night vision reference point located on another face of the lens, the second fitting point being positioned on a straight horizontal eye gaze direction when the user wears the progressive addition lens mounted in the frame with a null user head declination angle and that the position of the frame, lens, and temple remains fixed relatively to the user's face, the night vision reference point having an optical spherical power suitable for far vision in night time conditions, the night vision reference point being positioned on an eye gaze direction inclined by an upward eye gaze declination angle when the user wears the progressive addition lens mounted in the frame with a downward head declination angle equal in degrees and opposite in sign to the upward eye gaze declination angle without moving the frame relatively to the user's face, the progressive addition lens comprising a second optical spherical power variation between the second fitting point and the night vision reference point, an optical spherical power at the night vision reference point being lower than an optical spherical power at the second fitting point, and the first optical spherical power variation between the first fitting point and the near vision reference point being formed on a face of the progressive addition lens and the second optical spherical power variation is formed on another face of the progressive addition lens.
|