| CPC E21B 49/003 (2013.01) [E21B 43/2605 (2020.05); E21B 47/003 (2020.05); E21B 47/02 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
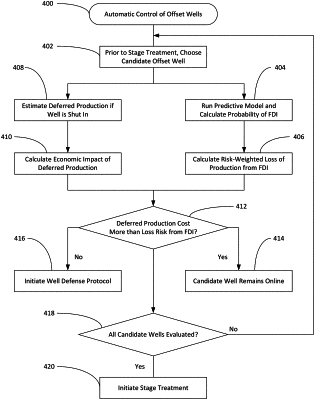
1. A method of controlling the operation of an offset well located near an active well that is undergoing a hydraulic fracturing operation that may produce a fracture driven interference (FDI) event to the offset well, wherein the method is intended to optimize the economic recovery of hydrocarbons from the active well and the offset well, the method comprising the steps of:
providing an FDI intervention system that includes a computer-implemented predictive model for determining a risk of the FDI event occurring during the hydraulic fracturing operation;
calculating a risk-weighted FDI event cost of the FDI event impacting production from the offset well;
calculating a defensive intervention implementation cost to apply a defensive intervention on the offset well to mitigate harm from the FDI event;
calculating a cost comparison based on a comparison of the defensive intervention implementation cost and the risk-weighted FDI event cost; and
automatically controlling the operation of the offset well with the FDI intervention system based on the cost comparison.
|