| CPC A61B 5/14552 (2013.01) [A61B 5/1455 (2013.01); A61B 5/1495 (2013.01); A61B 5/681 (2013.01); A61B 5/7203 (2013.01); G01K 13/00 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0238 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0271 (2013.01); A61B 2562/043 (2013.01); A61B 2562/046 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A method for performing a blood-oxygen saturation measurement using a wearable electronic device, comprising:
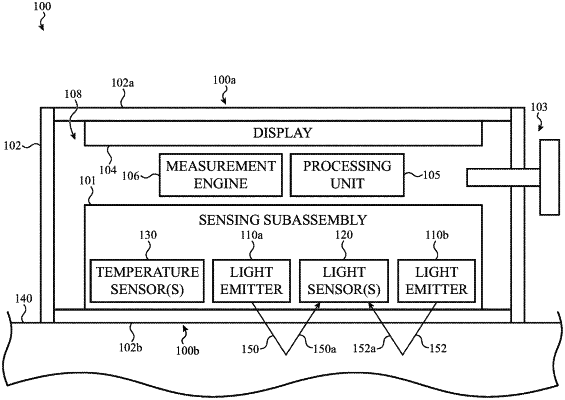
emitting light at a first wavelength and a second wavelength using one or more light emitters that are positioned in a first cavity of the wearable electronic device;
measuring a returned portion of the light that has interacted with a user using one or more light sensors that are positioned in a second cavity of the wearable electronic device;
sensing a temperature within an interior volume of the wearable electronic device using a temperature sensor that is positioned in a third cavity of the wearable electronic device, wherein the first cavity, the second cavity and the third cavity are separated by one or more walls;
determining a temperature difference between the sensed temperature and a nominal temperature;
determining a first wavelength offset by multiplying the temperature difference by a temperature coefficient calculated during a calibration processes of the wearable electronic device; and
determining, by a processor of the wearable electronic device, an estimated blood-oxygen saturation value based at least partially on the returned portion of the light, the first wavelength offset, and a drive current of the one or more light emitters.
|