| CPC A61B 5/0205 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0537 (2013.01); A61B 5/1116 (2013.01); A61B 5/1118 (2013.01); A61B 5/4875 (2013.01); A61B 5/7282 (2013.01); A61B 7/00 (2013.01); A61B 5/024 (2013.01); A61B 5/0816 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
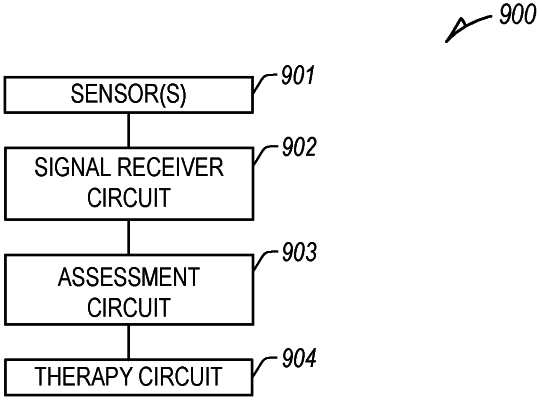
1. A system for determining patient dehydration during cancer therapy, comprising:
a signal receiver circuit configured to receive first and second physiologic information of a patient, the first physiologic information comprising heart sound information of the patient, and the second physiologic information comprising information different than the first physiologic information; and
an assessment circuit, coupled to a therapy circuit, the assessment circuit configured to:
determine an indication of patient dehydration associated with cancer therapy using the received first and second physiologic information; and
provide cancer therapy adjustment information at an output based on the determined indication of patient dehydration.
|