| CPC A61B 5/0205 (2013.01) [A61B 5/021 (2013.01); A61B 5/02416 (2013.01); A61B 5/0816 (2013.01); A61B 5/1135 (2013.01); A61B 5/6824 (2013.01); A61B 5/6826 (2013.01); A61B 5/7278 (2013.01); A61B 5/022 (2013.01); A61B 5/0235 (2013.01); A61B 5/02427 (2013.01); A61B 5/053 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0219 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0261 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
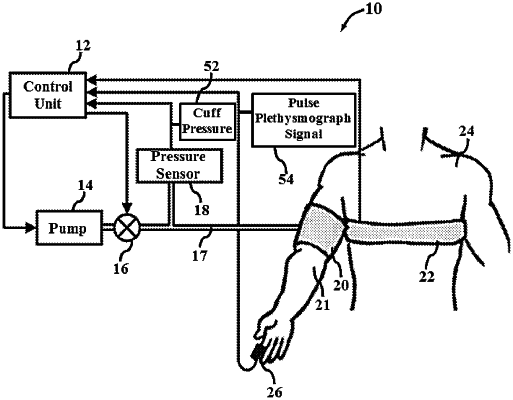
1. A non-invasive blood pressure variability measuring system (10), comprising: a cuff (20) pneumatically connected to a pump (14) to inflate the cuff (20) to be wrapped around a limb (21) of a subject (24);
a pressure sensor (18) associated with the cuff (20) for measuring a cuff pressure (52);
a photoplethysmogram sensor (26) attached to a fingertip in the same limb (21) of the subject (24) and placed to be distal to the cuff (20) for monitoring blood flow and recording a pulse plethysmograph signal (54); and
a control unit (12) connected to the pressure sensor (18) and the photoplethysmogram sensor (26),
the system (10) configured to measure a variation in systolic and diastolic blood pressures at a frequency corresponding to that of a respiratory cycle of the subject,
wherein the system is configured to either inflate the cuff (20) from a low pressure below the diastolic pressure or deflate the cuff from a pressure higher than the systolic pressure, in steps and hold the pressure at a constant level at every step for a duration of more than one respiratory cycle of the subject,
the control unit (12) configured to simultaneously record the cuff pressure (52) and the plethysmograph signal (54) such that an empirical relationship is derived between the cuff pressure (52) and an amplitude measure of the plethysmograph signal (54), and at the same time to assess a distribution of systolic and diastolic pressures, by obtaining variations in the plethysmograph signal during every pressure step,
wherein the empirical relationship between the cuff pressure (52) and the amplitude measure of the pulse plethysmograph signal (54) is nonlinear and is determined using a parametric curve fit, and the system is configured to yield a mean value curve and variation curves (85) providing a variation in pressure for each value of the pulse plethysmograph signal (54), wherein the mean value curve and the variation curves provide the distribution of the systolic and diastolic pressures,
wherein the empirical relationship between cuff pressure and pulse plethysmograph signal is determined by identifying a peak and trough in the pulse plethysmograph signal (54) and plotting an area under the curve (55) of each pulse plethysmograph signal (54) against the cuff pressure (52), wherein the area under each curve (55) indicates a volume of blood in the finger with each pulse, to yield the range of systolic and diastolic pressures.
|