| CPC H04W 74/0833 (2013.01) [H04W 72/0466 (2013.01); H04W 72/20 (2023.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
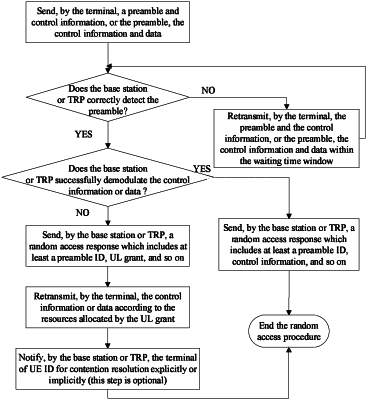
1. A wireless communication method, comprising:
receiving, by a network node, a random-access request from a terminal for an initial random-access procedure, wherein the random-access request comprises a preamble and a first data block, and wherein the first data block comprises control information that corresponds to an identifier of the terminal for contention resolution; and
transmitting, by the network node in response to the random-access request, a random-access response to the terminal,
wherein the initial random-access procedure completes successfully in response to the random-access response including a same control information as the random-access request, and
wherein, in case the random-access response fails to include the same control information as the random-access request, the random-access response comprises uplink grant information allocating an uplink resource for a second data block, the method further comprises receiving, by the network node, the second data block from the terminal upon the terminal receiving the random-access response and determining that the received random-access response fails to include the same control information as the random-access request.
|