| CPC H04L 63/1425 (2013.01) [H04L 61/4511 (2022.05); H04L 63/1416 (2013.01); H04L 63/1441 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
1. A method for detecting anomalies of a DNS traffic in a network comprising:
analysing, through a network analyser (11) connected to said network, each data packets exchanged in said network;
isolating, through said network analyser (11), from each of said analysed data packets a related DNS packet;
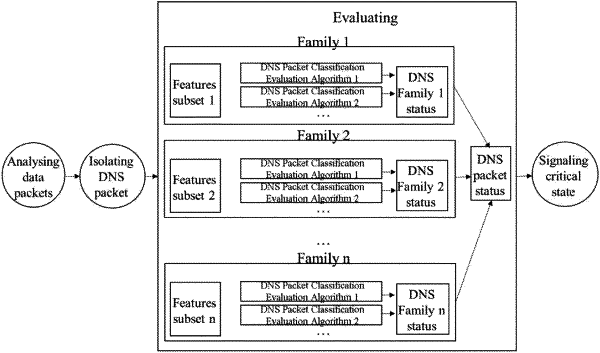
evaluating, through a computerized data processing unit (21), each of said DNS packets generating a DNS packet status;
signaling, through said computerized data processing unit (21), an anomaly of said DNS traffic when said DNS packet status defines a critical state;
wherein said evaluating further comprises:
assessing, through said computerized data processing unit (21), each of said DNS packet by a plurality of evaluating algorithms generating a DNS packet classification for each of said evaluating algorithms;
aggregating, through said computerized data processing unit (21), said DNS packet classifications generating said DNS packet status; and
wherein said critical state is identified when said DNS packet status is comprised in a critical state database stored in a storage medium (31); wherein said isolating further comprises extracting, through said computerized data processing unit (21), all the features from each of said DNS packet, wherein said assessing further comprises defining, through said computerized data processing unit (21), a plurality of family subsets of said features, wherein each of said plurality of evaluating algorithms generates a DNS packet classification from a sole family subset, wherein said aggregating further comprises generating, through said computerized data processing unit (21), a DNS family status grouping said DNS packet classifications of a same family subset according to a predefined family-logic evaluation, and wherein said aggregating further comprises generating, through said computerized data processing unit (21), said DNS packet status grouping said DNS family status according to a predefined packet-logic evaluation.
|